Why do your electric vehicles show significant differences in range and acceleration?
What is the core technology of an electric vehicle?
It is the essential “three electric” system—motor, battery, and control unit.
The motor is the “heart” of an electric car for power. If you want to know how Tesla vs Huawei vs BYD motors compare, click this link to learn more.
Today, let’s open up the discussion on the secrets of Tesla’s motor.
As a motor manufacturer with many years of experience, I know deeply that the choice of motor is critical for an electric vehicle’s performance. Behind the Tesla Model 3’s success is the clever combination of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and an induction motor.
So, what kind of motor configuration can balance both efficiency and power?
In this article, I will delve into the Tesla Model 3 motors technology and reveal how it enhances both range and performance.
Let’s first take a brief look at the motor configurations of the three models of the Tesla Model 3.
Before, we also looked at the Xiaomi SU7 Front Drive Motor, if you want to learn more, please click the link.
Motor Configurations of the Three Tesla Model 3 Models
This table lists the motor configurations of the three different models of the Tesla Model 3 in detail.
According to the table, we can see:
| Motor | Tesla Model 3 Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Model | Tesla Model 3 Long Range Model | Tesla model 3 Performance Model |
| Motor Model Number | 3D7 | Front 3D3 / Rear 4D2 | Front 3D3 / Rear 3D7 |
| Number of Drive Motors | Single Motor | Dual Motor | Dual Motor |
| Motor Layout | Rear | Front+Rear | Front + Rear |
| Motor Type | Permanent Magnet | Front Induction / Rear Permanent Magnet | Front Induction / Rear Permanent Magnet |
| Total Motor Power [kW] | 194 | 343 | 331 |
| Total Motor Horsepower [Ps] | 264 | 466 | 450 |
| Total Motor Torque [N·m] | 340 | 723 | 559 |
| Front Motor Max Power [kW] | – | 137 | 137 |
| Front Motor Max Torque [N·m] | – | – | 219 |
| Rear Motor Max Power [kW] | 194 | 265 | 194 |
| Rear Motor Max Torque [N·m] | 340 | 340 | 340 |
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Model:
Only equipped with a single permanent magnet synchronous motor. This configuration usually brings higher energy efficiency and a simplified drive system design. It reaches a maximum power of 194 kW, with a torque of 340 Nm.
Long Range Model:
Equipped with two motors, an induction motor on the front axle and a permanent magnet synchronous motor on the rear axle. This design, which mixes an induction motor with a permanent magnet synchronous motor, optimizes both acceleration performance and energy efficiency. It has a total power of 343 kW and a torque of 723 Nm, with the front motor reaching a maximum power of 137 kW.
Performance Model:
Also adopts a combination of an induction motor on the front axle and a permanent magnet synchronous motor on the rear axle, providing stronger power and acceleration performance. The total power is 331 kW, with a torque of 559 Nm, and the front motor power reaches 219 kW.
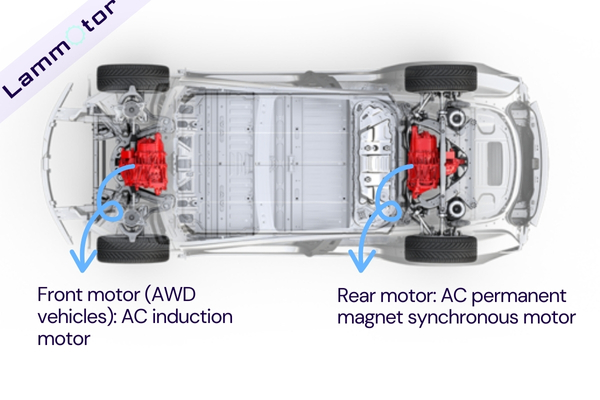
This diversity in configurations allows Tesla to offer customized solutions for different driving needs, whether one is pursuing ultimate performance or improved range.
After understanding the motor configurations of the three Tesla Model 3 models, you might be curious why Tesla chooses to use different types of motors in different models.
The induction motor, which was Tesla’s choice for its early models, has unique advantages and limitations.
So, what are the specific characteristics of an induction motor, and how does it impact vehicle performance?
Induction Motor
Tesla’s first mass-produced electric car was the Roadster, which was launched in 2008.
The Roadster used a traditional three-phase AC induction motor, modified from a Lotus Elise.
This motor type was a three-phase four-pole induction motor, with a rated voltage of 375V, offering high power and torque output.
The induction motor of the Roadster has a peak power of 185 kW and a rotational speed of up to 14,000 RPM, while its asynchronous induction motor reaches a peak power of 215 kW, a maximum rotational speed of 13,000 RPM, and a maximum torque of 430 Nm, with a power density of 2.25 kW/kg. These parameters together give the Roadster excellent performance.
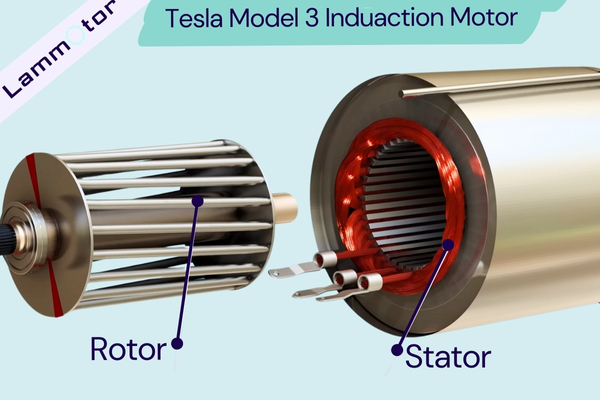
Following the Roadster, Tesla’s Model S launched in 2012 and the subsequent Model X SUV also used induction motors. The motor type during this period remained three-phase induction motors, with peak power and torque similar to the Roadster’s, reaching 215 kW and 370 Nm, with a peak speed still maintained at 14,000 RPM.
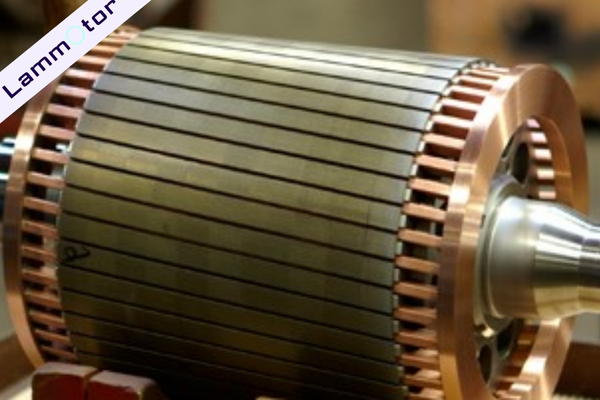

In 2014, Tesla revealed a copper rotor squirrel cage motor patent, showcasing its innovation in induction motor technology. This copper rotor’s manufacturing process is low-cost yet efficient, featuring a simple structure and high power, perfectly meeting Tesla’s demand for high-performance electric vehicles.
This motor design allows Tesla models like the Model S Plaid edition to achieve amazing acceleration performance—reaching 100 km/h from a standstill in just 2.1 seconds, with a top speed of 320 km/h.
So, what drives Tesla to continue using induction motors, even though electric vehicles in China tend to use lighter permanent magnet synchronous motors?
One of the main reasons Tesla continues to use induction motors is their lower cost and the fact that they do not require permanent magnets, thereby avoiding the risk of demagnetization.
First, induction motors do not need any permanent magnetic materials, which is particularly important in motor design. Permanent magnet materials like neodymium-iron-boron offer excellent performance but are costly and prone to demagnetization in high-temperature environments.
In contrast, induction motors use copper-core rotors, a design that is not only low in cost but also stable and reliable, eliminating concerns about high-temperature demagnetization.
However, the design of induction motors is not without its drawbacks.
One drawback of induction motors is their low efficiency at low speeds, and the rotor can easily overheat, which may restrict performance in electric vehicle applications. Compared to permanent magnet motors, asynchronous motors are less efficient at low speeds.
Therefore, starting from the third-generation electric drive system, the Model 3/Y first adopted an embedded permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
The permanent magnet motor used by Tesla is officially called an “interior permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor,” abbreviated as IPMSynRM. IPM stands for interior permanent magnet, Syn for synchronous, and RM for reluctance motor.
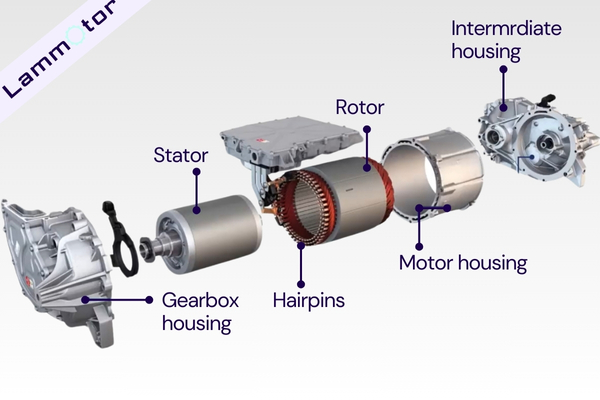
Why use it?
The permanent magnet synchronous motor has a size advantage.
The permanent magnet synchronous motor focuses on efficiency in the low-to-medium speed range, while the induction motor excels in high-speed efficiency and high torque.
Since the Model 3 is positioned as a mass-produced passenger car, it focuses more on efficiency (i.e., range) than on torque for acceleration, hence the use of an embedded permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Model S/X uses an induction motor for good reasons, and it’s not merely to save costs. The induction motor has greater power, facilitating faster acceleration from 0 to 100 km/h, and it continues to run smoothly without demagnetization even under long-term high-power and high-temperature operation.
While the permanent magnet motor has the obvious advantages of compact size and high efficiency, it does face demagnetization issues.
Permanent magnets tend to demagnetize under high temperatures and strong vibrations. Additionally, while running at low speeds and high power, even if the temperature is not high, the stator’s strong electromagnetic field can induce eddy currents in the rotor, causing demagnetization.
Interior Permanent Magnet Structure
The magnets in the IPMSynRM motor are embedded within the rotor core, rather than being surface-mounted.

Why design it this way?
Typically, to achieve maximum torque, the stator’s rotating magnetic field needs to stay 45 degrees ahead of the rotor’s magnetic field.
However, this control is not easy and requires significant circuit design.
It involves continuously detecting the rotor’s angle and speed, and then calculating the voltage, current, and phase of the three-phase electric field that generates the rotating magnetic field.
But a problem arises:
This rotor design provides high torque at low speeds, but at high speeds, the magnets are very close to the stator coil.
The strong magnetic field cuts through the stator coil, inducing a high back electromotive force, or back EMF, in the coil.
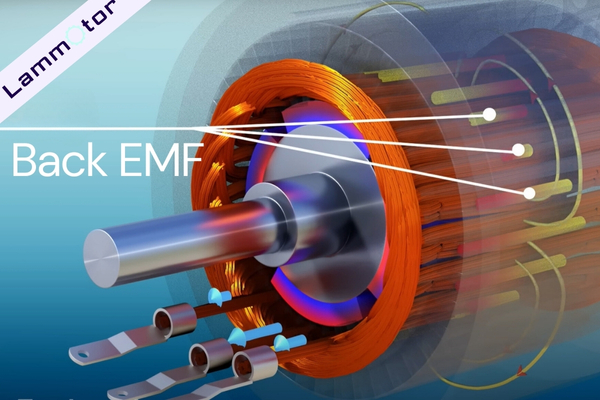
This back EMF will counter the drive voltage entering the stator, meaning that at high speeds, a much higher drive voltage is required.
So, the interior design is the best choice.
It not only enhances the motor’s mechanical strength but also improves performance through better thermal management, preventing the magnets from dislodging at high speeds.
The rotor of the synchronous motor has six axially V-shaped slots, with powerful “neodymium-iron-boron” rare earth magnets embedded in the V-shaped slots.
This is known as “interior permanent magnet—IPM,” with each set divided into two pieces, and each piece further divided into four sections. This division helps reduce “eddy current heating” since the magnet material, being neodymium-iron, can easily induce eddy currents in a swirling magnetic field, causing heating. Smaller magnet sections reduce eddy currents.
Not only the Tesla Model 3 but almost all EV and HEV synchronous motors use this method. However, the technology varies, mainly in the size, position, shape, and number of permanent magnets, which is the manufacturer’s proprietary secret.
Don’t underestimate these differences; every small change from principle, and design, to manufacturing requires a significant amount of software simulation and hardware testing. Everyone is core intellectual property for top manufacturers like Tesla, BMW, Benz, and Toyota.
Flat Wire Winding Technology
The 3D6 motor is Tesla’s first flat-wire motor, equipped in the 2022 Tesla Model 3.
Compared to previous motor models, this motor technology has made a substantial leap, with the windings changing from round wire to flat wire, achieving new highs in power density and torque density.
Both torque and speed have been improved, reaching 19,000 RPM and 440 Nm, respectively.
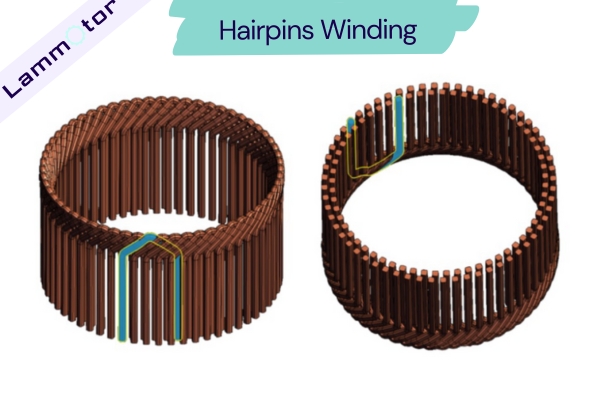

Currently, most motors use round wire, with round copper wires for the windings.
The advantages of a flat-wire motor over a round-wire motor include:
A 20% increase in slot fill rate, can reduce motor size.
The wider cross-section reduces resistance/temperature rise by around 50%/10%, providing higher output power, with a peak power density reaching 4.4 kW/kg, significantly higher than the current round-wire motors’ 3.2-3.3 kW/kg.
In motor losses, copper losses account for 65%. In flat-wire motors, the effective winding resistance decreases due to the improved slot fill rate, thereby reducing copper losses.
The Model Y, equipped with a flat-wire motor, has optimized both motor volume and power density. Tesla has currently launched five motor models in China, with the maximum power of the flat-wire permanent magnet synchronous motor increasing from 202 kW to 220 kW and maximum torque from 404 Nm to 440 Nm.
The rear motor of the Model Y adopts the flat-wire solution, with the flat wire’s enamel weight at about 5.78 kg, ensuring better welding consistency and fullness, as well as reducing the rotor volume and weight.
We expect that the Model 3 will follow suit, accelerating the adoption of flat-wire motors under demonstration effect, with automakers like BYD, NIO, Ideal, and Volkswagen also beginning to switch to flat-wire motors.
Oil Cooling Technology
From the Model S to the Model 3, cooling technology has switched from water cooling to oil cooling.
The early Model S used a water cooling system for motor thermal management, but because it cooled the casing and did not directly cool the windings, the cooling efficiency was low.
So, what technology did Tesla adopt later?
The answer is oil cooling, which significantly enhances cooling capability and motor power density.

The Tesla Model 3 adopts a “stator cooling + rotor cooling” composite solution. Oil holes are opened in the yoke part, and cooling oil first passes through these oil holes and then sprays onto the winding ends.
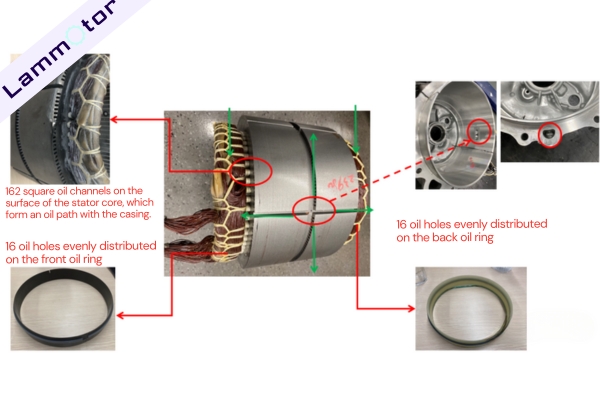
The stator core surface has 162 square oil channels that form an oil circuit with the casing, and plastic oil rings with 16 oil holes evenly distributed around the circumference are installed at both ends for spray cooling of the winding ends.
The rotor shaft is hollow and has oil-splashing holes, allowing active rotor cooling and, through rotor oil-splashing, achieving inner ring cooling of the stator winding.
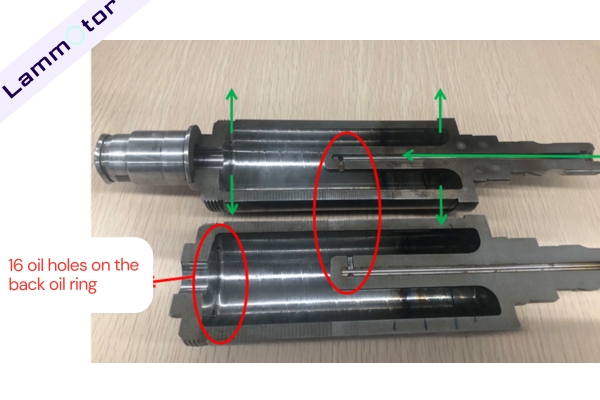

The Model 3’s composite oil cooling technology significantly improves the motor’s power density and torque density. Compared to ordinary water-cooled motors, the continuous torque can be increased by 40-50%.
Contact us for Manufacturing New Energy Motor Stator Cores.
Now, we have a detailed understanding of the motor used in the Model 3. We focused on the unique features of the induction motor and permanent magnet synchronous motor, and how they work together to enhance electric vehicle performance and range.
Through an analysis of the Tesla Model 3 motors, we can see that Tesla adopts diverse motor solutions to meet different user needs. This not only demonstrates flexibility in motor design but also reflects Tesla’s technical foresight in the field of electric vehicles.
What do you think the future of electric vehicle motor technology will look like? Will it focus more on efficiency or pursue stronger power performance? Please share your thoughts in the comments.
If you need custom new energy motor stators and rotors, feel free to contact us. We are a professional motor core manufacturer in China with many years of experience, offering sample and mass production of stator cores.