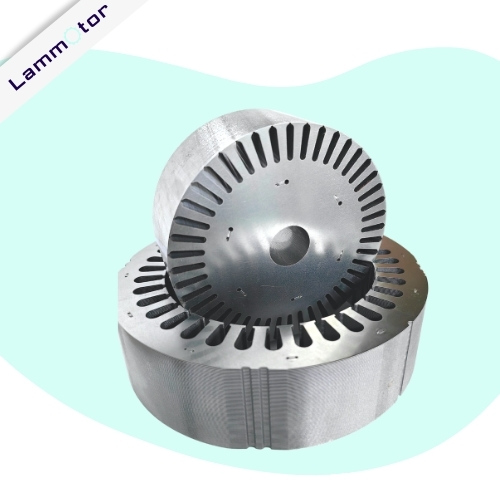
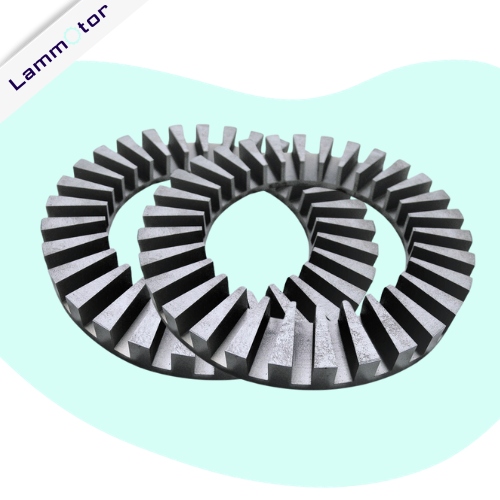
Transformer Laminations in China
Lammotor is a leading manufacturer of silicon steel cores for the transformer industry in China. We specialize in producing top-quality laminations for transformers, inverters, reactors, and rectifiers. With our expertise, we are renowned for manufacturing high-performance transformer cores, toroidal cores, and other electrical stampings.
Trust Lammotor for reliable and efficient transformer laminations tailored to meet your specific requirements, ensuring superior energy efficiency and durability in all your electrical applications.
Customize Transformer Core Laminations
A transformer is an essentially electrical device that transfers electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. It’s widely used in power distribution, industrial machinery, and electronics. In transformer core construction, to hold the coil windings, individual laminations are stamped from larger sheets of steel and formed into thin strips that resemble the letters “E,” “L,” “U,” and “I.”
At Lammotor, we specialize in customizing transformer core laminations to your exact specifications. We can produce various types of laminations, such as E-type, EI, UI, and EE laminations. Our advanced manufacturing capabilities allow us to quickly turn around all projects, including prototypes based on customer designs.
Materials Used in Transformer Laminations
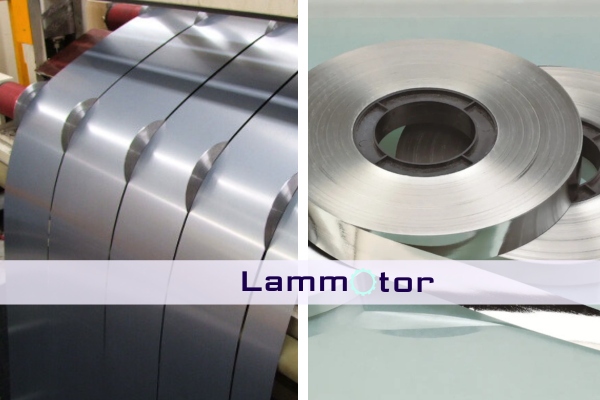
Transformer laminations require high-quality materials to ensure efficiency and durability. We provide a range of specialized materials to meet diverse application needs:
Electrical Steel: We offer laminations made from Non-Grain Oriented (NGO) steel for applications requiring uniform magnetic properties, Grain Oriented (GO) steel for high-efficiency transformers and Cold Rolled Motor Lamination (CRML) steel for motors and transformers requiring precise control.
Amorphous Alloy: Ideal for reducing core losses, amorphous alloys provide exceptional energy efficiency in modern transformers.
Nickel-Iron or Iron-Cobalt Alloys: These materials are used for high-performance applications requiring superior magnetic properties and minimal energy loss.
Manufacturing Capability of Transformer Core

Laminations Stamping for Mass Production
For large-scale manufacturing, laminations are typically produced using high-speed stamping machines. These machines punch out the required shapes from thin sheets of electrical steel with great accuracy. This method is highly efficient and cost-effective for producing large volumes of laminations, ensuring consistent quality across all units.

Laser Cutting Lamination for Prototyping
When developing prototypes or small batches, laser cutting is the preferred method. Laser cutting provides flexibility and precision, allowing for the creation of intricate designs without the need for expensive tooling. This process is ideal for custom transformer designs where unique shapes and sizes are required.
Other Products
FAQs
Transformer core laminations play a critical role in reducing energy losses due to eddy currents. There are several types of laminations used in transformer cores, each designed to optimize performance and efficiency.
EI Laminations: These are the most common and are characterized by their E and I-shaped sections. They are often used in low-frequency transformers and provide a balance between efficiency and cost.
UI Laminations: These laminations have U and I shapes, allowing for easy assembly and disassembly. They are typically used in large transformers where easy maintenance is necessary.
Toroidal Laminations: These are donut-shaped and provide minimal magnetic leakage, leading to higher efficiency. Toroidal transformers are compact and used in sensitive electronic equipment.
C-Laminations: Known for their C-shaped sections, these laminations are used in transformers requiring a higher magnetic flux density.
Each type of lamination is chosen based on the specific requirements of the transformer application.
Transformer core laminations are used to reduce eddy current losses and improve efficiency in electrical transformers. They are essential in power transformers, distribution transformers, and high-frequency transformers.
Silicon steel laminations help maintain magnetic properties, minimize heat generation, and optimize energy transfer in applications ranging from electrical grids to industrial machinery and consumer electronics.
The thickness of transformer lamination typically ranges from 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm, depending on the application.
Thinner laminations, around 0.2 mm, are used in high-frequency transformers to reduce eddy current losses, while thicker laminations, up to 0.5 mm, are common in power transformers for lower-frequency applications.
Silicon steel laminations are stacked at up to 300 pieces per minute, either manually or automatically, with full interleaving.
The core is usually made of E-shaped or U-shaped structures stacked with silicon steel sheets. Before winding, the core should be cleaned to ensure that there are no foreign objects or impurities. Primary coil winding and secondary coil winding are usually performed.
The primary coil (primary winding) is usually wound first. According to the design requirements, the wire is evenly wound on the specified position of the core, paying attention to the precise control of the number of turns and direction.
The secondary coil (secondary winding) is carried out after the primary coil is wound. The number of turns and wire diameter of the secondary coil are designed according to the output voltage and current requirements of the transformer.
If the transformer is designed as a multi-layer winding, a layer of insulating material needs to be added after each layer is wound to prevent short circuits between layers.
Get a Quote for Your Transformer Lamination Needs
Ready to start your project? Contact Lammotor for a free, no-obligation quote tailored to your specific transformer lamination requirements. Simply fill out our quick online form or reach out to our expert team directly. We ensure fast turnaround times and competitive pricing for all your custom lamination needs.