Have you ever wondered what keeps humanoid robots moving so gracefully? As a manufacturer with years of experience in crafting coreless motors lamination stacks, I can tell you that the secret lies in the motor at its core—literally!
Different types of robots require various motors, such as servo motors and stepper motors for industrial robots. However, in humanoid robots, coreless motors, especially frameless torque motors for the torso and coreless cup motors for the dexterous hand joints, are the real stars. These motors provide the agility and precision needed to mimic human movements.
Coreless DC motors, known for their precision and efficiency, are the unsung heroes behind these lifelike movements. Today, I’m here to share why coreless motors are truly the heartbeat of every joint and limb of humanoid robotics.
What Are Coreless Motors?
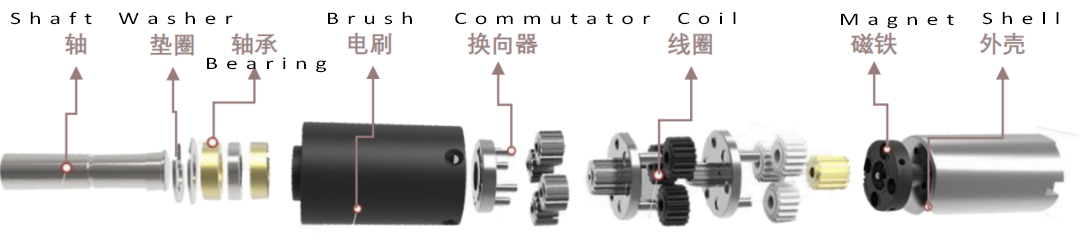
Coreless motors, often called cup motors due to their unique rotor structure, are a type of miniature DC permanent magnet servo motor. Unlike traditional motors, the rotor in a coreless motor is shaped like a cup, which is why it’s known as a “cup” motor.
The key components of a coreless brushed DC motor include bearings, a shaft, brushes, a commutator, the cup-shaped winding (rotor), magnets (stator), coils, and the outer casing.
What sets the coreless motor apart is its ironless rotor, making it incredibly lightweight and compact. Typically, these motors have a diameter of no more than 40mm, making them ideal for applications requiring precision and efficiency, such as humanoid robots.
Coreless Motors vs. Traditional DC Motors: What’s the Difference?
The primary difference between coreless motors and traditional DC motors lies in the absence of an iron core.
In traditional brushed DC motors, the rotor is a coil wound around an iron core, which creates magnetic resistance and can cause electromagnetic interference. Coreless motors, on the other hand, eliminate the iron core, with the rotor consisting solely of precisely wound coils. This design minimizes magnetic hysteresis, reduces electromagnetic interference, and allows for significantly higher rotational speeds.
Additionally, coreless motors experience no cogging torque, leading to smoother operation and higher energy conversion efficiency—over 75%.
With a higher energy density, coreless motors can be up to 50% lighter than traditional motors of the same power, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and high-performance motors.
Advantages of Coreless DC Motors
Coreless motor offers a range of advantages that make them ideal for applications in humanoid robotics. Let’s delve into these benefits:
1. Low Starting Torque
Coreless motor has a low starting torque due to the absence of hysteresis losses and cogging effects. At startup, the bearing load is typically the only resistance, allowing for smooth and low-speed operation. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for applications like wind turbines, where low startup wind speeds are desirable.
2. No Radial Forces Between Rotor and Stator
A unique feature of coreless motor is the absence of radial forces between the rotor and stator, as there are no stationary silicon steel sheets. This is vital in critical applications, where radial forces could destabilize the rotor. By reducing these forces, coreless motors enhance rotor stability, contributing to the overall reliability of the motor.
3. Smooth Speed Curve and Low Noise
Without slotted silicon steel sheets, coreless motors experience reduced torque and voltage harmonics. Additionally, the absence of AC fields eliminates AC noise, leaving only noise from bearings, airflow, and non-sinusoidal current vibrations. This results in a smoother speed curve and significantly lower noise levels, which is crucial for applications requiring quiet operation, such as in humanoid robots or medical devices.
4. High-Speed Brushless Coils
At high speeds, a low inductance value is necessary, which in turn lowers the startup voltage. Coreless motors achieve this by increasing the number of poles and reducing the thickness of the casing, which also decreases the motor’s weight and increases power density.

5. Quick Response Brushed Coils
In brushed coreless dc motor, the low inductance of the copper plate coils ensures that the current responds quickly to voltage fluctuations. With a low rotational inertia, the torque response is quick, making the rotor’s acceleration twice as fast as that of traditional motors. This is particularly advantageous in applications requiring rapid and precise movements.
6. High Peak Torque
Coreless motors can achieve a high peak torque relative to continuous torque because the torque constant remains unchanged as current peaks. This linear relationship between current and torque allows coreless motors to produce significantly higher peak torques compared to traditional motors, which tend to plateau when saturated.
7. Sine Wave Induced Voltage
Due to the precise positioning of the coils, coreless motors generate low voltage harmonics. The structure of the copper plate coils in the air gap produces a smooth induced voltage waveform. Sine wave drives and controllers enable the motor to generate smooth torque, which is particularly useful in slow-moving objects like microscopes, optical scanners, and robots where precise position control is crucial.
8. Excellent Heat Dissipation
The design of the coreless motor allows for air to flow across both the inner and outer surfaces of the copper plate coils, leading to better heat dissipation compared to slotted rotor coils. For traditional motors, the coils are embedded in silicon steel slots, which restricts airflow and increases heat buildup. In contrast, coreless motors maintain lower temperature rises for the same output power, making them more efficient and reliable over prolonged use.
In conclusion, coreless dc motors stand out for their energy efficiency, superior control, stability, and reliability. These features make them an ideal choice for the complex and demanding applications found in humanoid robotics.
Applications of Coreless Motors in Humanoid Robots
Coreless motor products have a wide range of downstream application scenarios, including medical, aerospace, industrial automation, humanoid robots, etc. In humanoid robots, coreless motors are mainly used for the dexterous hand joint motors of humanoid robots.

The flexibility and precision required for tasks like gripping and manipulating objects demand motors that can deliver high torque, power density, and control accuracy—all characteristics of coreless motors. In humanoid robots, especially in the hands, these motors enable a high degree of freedom and precise motion control.
A prime example is Tesla’s Optimus robot, where coreless motors are crucial for the hand’s movement.
The Optimus dexterous hand is mainly composed of hollow cup motors, precision planetary reducers, ball screws, sensors and encoders. The hollow cup motor accounts for 54.5% of the cost of all parts of the hand actuator and is the most critical component.
The hollow cup motor enables the fingers to move. Each dexterous hand is driven by 6 motors. The thumb is equipped with 2 hollow cup motor modules, which can complete the two actions of extension and flipping at the same time.
Conclusion: Why Coreless Motors Are the Future of Humanoid Robotics
Coreless motor is undeniably critical to the evolution of humanoid robots. Their unique combination of high efficiency, precision, and compact design makes them the ideal choice for applications requiring agility and accuracy, particularly in the intricate hand movements of humanoid robots.
The global market for coreless motors is dominated by giants like Switzerland’s Maxon and Portescap, and Germany’s Faulhaber, which together hold over half of the market share. However, the competition is fierce, with emerging companies from China, such as Mige Electric and Topband, making significant strides in this field.
As humanoid robots continue to advance, coreless dc motor will play an increasingly pivotal role in their development and widespread adoption.
We are a leading coreless motor lamination stacks manufacturer in China, offering customized solutions to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to learn how we can support your projects with our high-quality products!