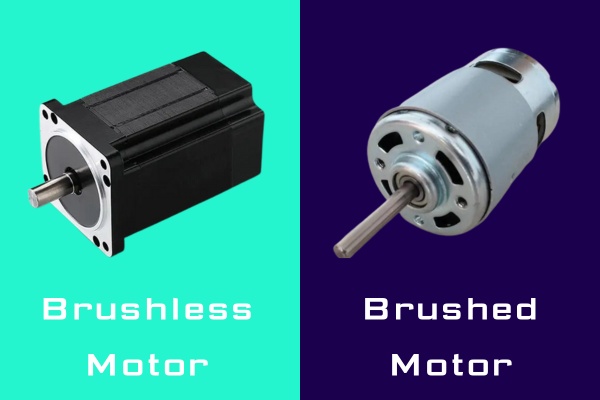
Brushless VS Brushed DC Motors: What’s the Difference? When it comes to electrical DC motors, there are two primary types: brushed and brushless motors. Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right motor for a specific application. This article will explore the working principles, pros and cons, applications, and key distinctions between brushed and brushless DC motors.
How Does a DC Electric Motor Work?
A DC electric motor, or a direct current electric motor, is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. It operates based on the principles of electromagnetism and the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents. The fundamental components of a DC motor include a stationary part called the stator and a rotating part known as the rotor.
The stator consists of one or more sets of electromagnets, which are coils of wire wrapped around a core. These electromagnets create a fixed magnetic field within the motor. On the other hand, the rotor contains a cylindrical structure with multiple windings, armature windings, and a commutator. The commutator is a segmented cylindrical conductor that reverses the current direction in the armature windings.
When an electric current is supplied to the armature windings, it creates a magnetic field around the rotor. The stator’s magnetic field interacts with the rotor’s magnetic field, causing a force that results in rotational motion. The commutator ensures that the direction of the current flowing through the armature windings is continuously reversed, creating a constant torque that keeps the motor running.
A power supply and a control circuit are used to control the speed and direction of a DC motor. By varying the voltage applied to the motor and adjusting the timing of the current reversal, the speed and direction of the motor can be regulated.
Overall, the functioning of a DC electric motor relies on the interaction between the magnetic fields generated by the stator and the rotor. This electromagnetic interaction converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, making DC motors widely used in various applications, including industrial machinery, automobiles, appliances, and robotics.
Brushed DC Motors
Brushed DC motors operate based on a simple design consisting of a rotor and a stator. Inside the motor is a commutator and brushes that make physical contact with the rotor’s armature. The brushes supply electrical current to the armature, generating a magnetic field that interacts with the fixed magnets in the stator, resulting in rotational motion.

Advantages
Cost-effective: Brushed DC motors are generally more affordable compared to brushless motors.
Simple control: The commutation system of brushed motors allows for straightforward speed and direction control.
Wide voltage range: They can operate on a wide range of voltages, making them versatile for various applications.
Disadvantages
Limited lifespan: The brushes in brushed motors wear down over time and require periodic maintenance or replacement.
Higher maintenance: The commutator and brushes need regular cleaning, and the wear and tear of the brushes can lead to performance degradation.
Lower efficiency: Brushed motors tend to be less efficient than brushless motors due to energy losses in the brushes and commutator.
Related Article: Difference Between Synchronous Motor And Induction Motor A Comprehensive Guide To Different Types Of Electric Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors, or BLDC motors, employ electronic commutation instead of physical brushes. The stator contains fixed magnets, while the rotor comprises multiple permanent magnets. The motor’s control system uses sensors to detect the rotor position and precisely energizes the stator windings to produce rotation.

Advantages
High efficiency: Brushless motors eliminate the energy losses associated with brushes and commutation, resulting in increased efficiency.
Longer lifespan: Without brushes to wear out, brushless motors generally have a longer operational lifespan.
Low maintenance: Brushless motors require minimal maintenance compared to brushed motors due to the absence of brushes.
Disadvantages
Higher cost: Brushless motors are typically more expensive than brushed motors due to their advanced control systems and electronic components.
Complex control: The electronic commutation system requires sophisticated control algorithms and dedicated motor controllers.
Limited voltage range: Brushless motors have a narrower voltage range than brushed motors.
Key Differences between Brushed and Brushless Motors
Brushless VS Brushed DC Motors, the difference between the two is that a brushless DC motor uses electronic commutation, meaning it has to have digital control to achieve commutation. A brushed DC motor is through carbon brushes to commutate and can be controlled by using traditional analog circuits such as thyristor, which is relatively simple.
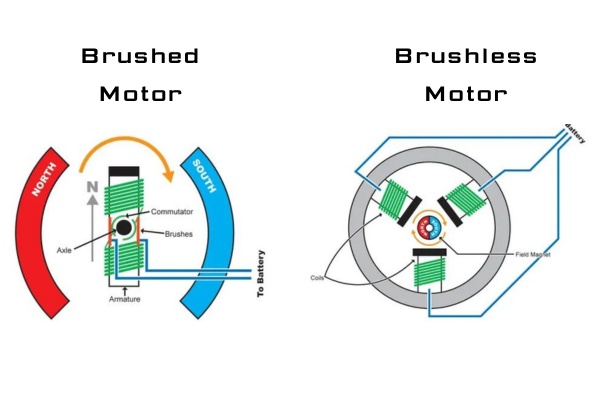
Commutation: Brushed motors use physical brushes and commutators for commutation, while brushless motors utilize electronic commutation.
Maintenance: Brushed motors require regular maintenance due to brush wear, whereas brushless motors have minimal maintenance requirements.
Efficiency: Brushless motors are generally more efficient than brushed motors due to the absence of brushes and commutation losses.
Lifespan: Brushless motors have a longer operational lifespan compared to brushed motors.
Cost: Brushed motors are typically more cost-effective, while brushless motors are more expensive.
Applications of Brushed and Brushless DC Motors
Brushed Motors:
Toys: Brushed motors are commonly found in remote-controlled cars, airplanes, and other battery-operated toys.
Power Tools: Many power tools, such as drills, electric screwdrivers, and jigsaws, utilize brushed motors for their cost-effectiveness.
Automotive Systems: Brushed motors are employed in vehicles’ windshield wiper systems, power windows, and seat adjustment mechanisms.
Appliances: Some household appliances, including fans, blenders, and vacuum cleaners, utilize brushed motors for their simplicity and affordability.

Brushless Motors:
Drones: Brushless motors are widely used in drones due to their high efficiency, precise control, and compact size.
Electric Vehicles: Brushless motors power electric vehicles, providing efficient and reliable propulsion systems.
Robotics: Many robotic systems, including industrial robots and humanoid robots, rely on brushless motors for precise motion control.
Industrial Automation: Brushless motors find applications in various automated systems, such as conveyor belts, CNC machines, and robotic arms.
Precision Equipment: Brushless motors are used in medical equipment, optical systems, and scientific instruments that require high precision and reliability.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of both brushed and brushless DC motors in a wide range of industries. The choice between the two depends on factors such as cost, efficiency, maintenance requirements, and the application’s specific needs.
Conclusion
Did you know brushless VS brushed DC motors? In the comparison between brushed and brushless DC motors, it is evident that both types have their strengths and weaknesses. Brushed motors offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, whereas brushless motors excel in terms of efficiency and durability. The choice between the two depends on the application’s specific requirements, considering factors such as cost, maintenance needs, efficiency, and lifespan.
Let Lammotor Help You Produce High-Quality Electrical Motor Laminations for Your Application!
Are you in need of high-quality electrical motor laminations for your application? Look no further than Lammotor. We specialize in producing top-notch laminations that meet the highest industry standards. Whether you require brushed or brushless motor laminations, our expert team is here to assist you.
With state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and a commitment to excellence, Lammotor is dedicated to delivering precision-engineered laminations that optimize motor performance and efficiency. Our laminations are crafted using the finest materials and advanced techniques, ensuring durability and reliability.
By partnering with Lammotor, you can benefit from our extensive experience and expertise in the field. We work closely with our clients to understand their unique requirements and provide tailored solutions that meet their specific needs. Our team of skilled professionals is equipped to handle projects of all sizes, from small-scale applications to large-scale industrial projects.
Contact us today and discover how we can meet your lamination needs with precision and excellence. Together, we can power your success!
FAQs
Can I Replace A Brushed Motor With A Brushless Motor?
It is possible but may require modifications to the motor mounting, control circuitry, and power supply.
Are Brushless Motors More Efficient Than Brushed Motors?
Yes, brushless motors are generally more efficient due to the absence of brushes and commutation losses.
Which Motor Type Is More Expensive?
Brushless motors are more expensive than brushed motors due to their advanced control systems.
Can Brushed And Brushless Motors Be Used Interchangeably?
In most cases, the two motor types are not interchangeable due to control and power requirements differences.
Are Brushless Motors Quieter Than Brushed Motors?
Yes, brushless motors are typically quieter than brushed motors due to the absence of brushes and commutator noise.