Servo motors are the unsung heroes powering countless machines around us, from industrial robots to everyday appliances. The choice between AC servo motor and DC servo motor can make a significant impact on your applications. So, you need to learn about the difference between AC Servo Motors and DC Servo Motors. It is crucial to select the right one for your specific needs.
A servo motor is a precise electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. Servo motor cores include laminated stator and rotor assemblies. The stator consists of multiple laminations, with windings that produce a rotating magnetic field when energized. Meanwhile, the rotor, also laminated, responds to this field, resulting in controlled motion essential for various industrial and automation applications.
AC Servo Motors: Overview and Types
AC servo motors are electrical devices designed to accurately control angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. They operate on alternating current (AC) and are widely used in various industries for their precision and efficiency.
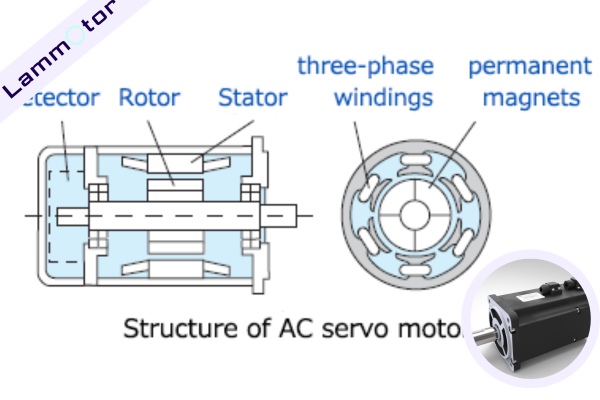
Induction AC Servo Motor
Induction AC servo motors utilize electromagnetic induction to create a rotating magnetic field, which drives the rotor.
High Torque: This induction motor is suitable for applications requiring high torque output at low speeds.
Cost-Effectiveness: Generally more affordable compared to other servo motor types.
Robust Construction: Durable and reliable, making them suitable for industrial environments.
Simple Control: Easy to control and integrate into various systems.
Low Maintenance: Minimal maintenance requirements due to their rugged design.
Synchronous AC Servo Motor
Synchronous AC servo motors maintain synchronism between the rotor and stator magnetic fields.
Precise Control: Accurate control over speed and position, ideal for high-precision applications.
High Efficiency: Efficient operation due to synchronous operation.
Smooth Operation: Provide smooth and consistent performance, reducing vibrations and noise.
Wide Speed Range: Capable of operating at various speeds without sacrificing performance.
Compact Design: Space-saving design, suitable for applications with limited space constraints.
Applications where AC Servo Motors Excel
AC servo motors find wide-ranging applications across various industries due to their precision, efficiency, and versatility. Some common areas where AC servo motors excel include:
Industrial Robotics: Used for precise control of robotic arms and actuators in manufacturing processes.

CNC Machining: Employed in computer numerical control (CNC) machines for accurate positioning and motion control.
Automated Packaging: Utilized packaging machinery for precise filling, sealing, and labeling operations.
Textile Machinery: Integrated into textile equipment for precise yarn tensioning and fabric handling.
Medical Devices: Applied in medical equipment for precise movement control in imaging systems and surgical robots.
If you would like servo motor vs stepper motor, please click the link.
DC Servo Motors: Overview and Types
DC servo motors are electrical devices that operate on direct current (DC) and are designed to provide precise control over position, velocity, and acceleration. They are widely used in various applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. DC servo motors come in two main types:
Brushed DC Servo Motor
Operation: These motors feature a rotor with a commutator and brushes that come into contact with the rotor windings, creating a magnetic field.
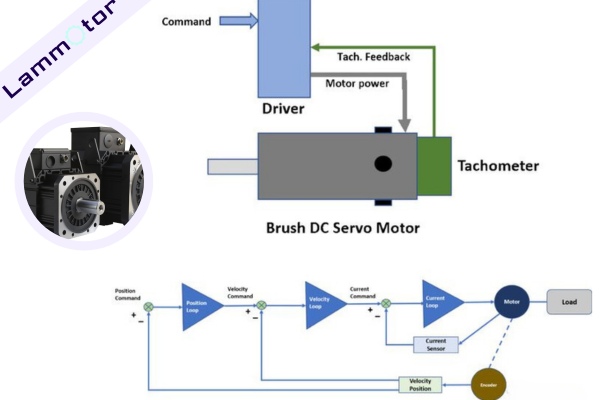
Features:
- Simple design and construction.
- Cost-effective compared to brushless motors.
- Easy to control and integrate into systems.
- Suitable for applications with moderate precision requirements.
- Require periodic maintenance due to brush wear.
Brushless DC Servo Motor (BLDC)
Operation: BLDC motors utilize electronic commutation instead of brushes and a commutator, improving efficiency and reliability.
Features:
- Higher efficiency and power density compared to brushed motors.
- Maintenance-free operation due to the absence of brushes.
- Precise control over speed, position, and torque.
- Reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) and noise.
Ideal for high-performance applications requiring high precision and reliability, such as robotics, aerospace, and medical devices.
DC servo motors, both brushed and brushless, offer versatile solutions for various industrial, commercial, and consumer applications requiring accurate motion control and high reliability.
Applications where DC Servo Motors Excel
DC servo motors, with their precise control and reliability, find extensive use in a wide array of applications across industries. Some notable areas where DC servo motors excel include:
Automotive Systems: Suitable for automotive actuators, power steering systems, and electric vehicles for precise control over motion and speed.
Aerospace: Ideal for aircraft control surfaces, UAVs, and satellite positioning systems due to their lightweight design and precise control capabilities.
Consumer Electronics: Used for cameras, printers, and drones for smooth and accurate motion control.
Medical Devices: Utilized in medical pumps, surgical instruments, and prosthetic limbs for precise movement control.
Industrial Automation: Applied in conveyor systems, pick-and-place machines, and packaging equipment for precise positioning and motion control.
Key Differences between AC and DC Servo Motors
Servo motors, whether AC or DC, are critical components in automation and motion control systems. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right motor for specific applications.
| Aspect | AC Servo Motors | DC Servo Motors |
| Power Source | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Control Systems | Closed-loop control system with encoders | Can utilize both closed-loop and open-loop systems |
| Feedback Mechanism | Typically employs encoders for precise feedback | Can use encoders or tachometers |
| Speed Regulation | Frequency and voltage control | Voltage control |
| Speed and Torque | Higher speeds, Higher torque | Limited torque and speed |
| Weight & Size | Relatively light in weight and small in size | Bulky and heavy |
| Noise & Operation | Generally operates quietly | May produce more audible noise |
| Efficiency | Typically higher efficiency | Can be efficient, especially in brushless versions |
| Stability | High control precision, better stability than DC servo motor | Low control precision and response speed, and relatively high stability Difference |
| Maintenance | High control precision, and better stability than DC servo motor | May require periodic maintenance for brushed versions |
Power Source: AC vs. DC
AC servo motors operate on alternating current, typically derived from mains power or inverters.
DC servo motors, as the name suggests, run on direct current, commonly sourced from batteries or rectifiers.
Control Systems: Closed-loop vs. Open-loop
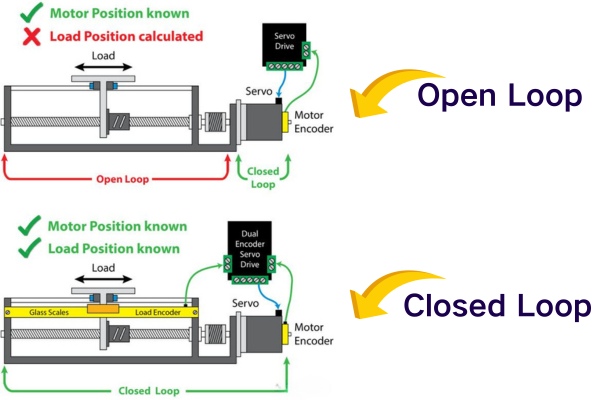
AC servo motors often employ closed-loop control systems, where feedback from encoders is used to adjust motor performance in real time, ensuring precise positioning and speed control.
DC servo motors can utilize both closed-loop and open-loop control systems. While closed-loop systems are common for high-precision applications, open-loop control may suffice for simpler tasks.
Feedback Mechanism: Encoders vs. Tachometers
AC servo motors typically incorporate encoders as feedback devices, providing accurate position and velocity feedback to the control system.
DC servo motors can use encoders as well, but they may also utilize tachometers, which measure motor speed, as a feedback mechanism.
Speed Regulation Method
AC servo motors employ frequency and voltage control methods to regulate speed, ensuring smooth operation across a wide range of speeds.
DC servo motors use voltage control to regulate speed, with variations in voltage directly affecting motor speed.
Speed and Torque
AC servo motors generally offer higher speeds and higher torque compared to DC servo motors.
DC servo motors typically provide limited torque and speed.
Weight & Size
AC servo motors are relatively light in weight and small in size. DC servo motors are bulky and heavy.
Noise & Operation
AC servo motors tend to operate more quietly due to smoother speed control and fewer mechanical components.
DC servo motors may produce more audible noise, especially in brushed versions, due to the presence of brushes and commutation.
Efficiency
AC servo motors are less efficient. Their efficiency is usually ranging from 5% to 20%.
DC servo motors can be efficient, especially brushless versions, but may experience losses due to friction in brushed versions.
Stability
AC servo motors offer excellent stability and accuracy, especially in closed-loop systems, making them suitable for high-precision applications.
DC servo motors also provide good stability but may require careful tuning in closed-loop systems to achieve similar performance.
Maintenance
AC servo motors typically have longer brush life and no commutator, so less maintenance is required.
DC servo motors with brushes may require periodic maintenance to replace worn brushes and commutators.
Conclusion
So there you have it! The world of servo motors, with its AC and DC varieties, is vast and full of possibilities. Whether you’re fine-tuning a robotic arm’s precision or controlling a CNC machine’s speed, understanding the differences between AC and DC servo motors is key.
From their power sources to their torque capabilities and even their size, each type brings its own set of advantages and considerations to the table.
So, next time you’re embarking on a new project, remember to choose wisely and let the motors do the talking!