Porsche has long been the gold standard in sports cars—combining stunning design with outstanding performance. But how does their first electric sports car, the Taycan, stack up when it comes to motor technology? In this article, we’ll break down the design and features of the Porsche Taycan motor, and take a brief look at how it compares with one of its fastest rivals—the Xiaomi SU7 Ultra.
Porsche Taycan Electric Drive Specifications
Taycan Turbo Motor System

- Combined peak power (front + rear): 500 kW
- Combined max torque: 850 Nm (300 + 550 Nm)
- Max motor speed: 16,000 rpm
- Front axle: Single-speed gearbox (8.05 ratio)
- Rear axle: Two-speed transmission (ratios: 16 and 8.05)
- 0–100 km/h: 3.2 seconds
- 0–200 km/h: 10.6 seconds
- Top speed: 260 km/h
Taycan Turbo S Motor System

- Combined peak power (front + rear): 560 kW
- Combined max torque: 1050 Nm (440 + 610 Nm)
- Max motor speed: 16,000 rpm
- Front axle: Single-speed gearbox (8.05 ratio)
- Rear axle: Two-speed transmission (ratios: 16 and 8.05)
- 0–100 km/h: 2.8 seconds
- 0–200 km/h: 9.8 seconds
- Top speed: 260 km/h
Porsche Taycan Motor Configuration and Design
Porsche didn’t choose induction motors—which are more focused on quick acceleration—for the Taycan. That’s because as a pure electric sports car, the Taycan needs to perform like a gas-powered sports car, even under repeated hard acceleration and braking. In these tough conditions, permanent magnet motors are more stable and more efficient overall.
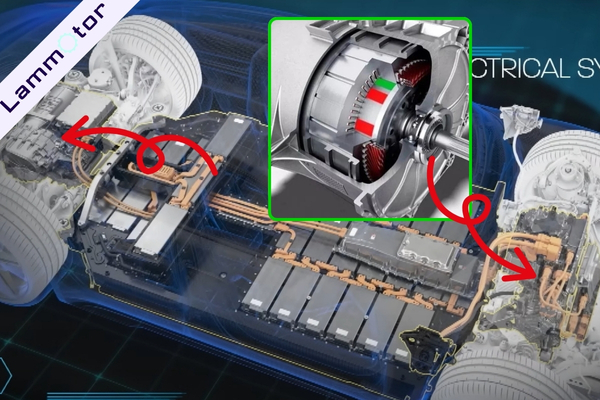
The Taycan is powered by two Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs), with one on the front axle and one on the rear—providing all-wheel drive.
Porsche uses a highly integrated design that combines the PMSM, gearbox, and pulse-controlled inverter into one compact drive unit.
The rear motor is mounted parallel to the axle, while the front motor connects directly to the drive shaft.
Unlike the AC induction motors used in models like the Tesla Model S, the Taycan’s permanent magnet motors offer several advantages: higher power density, higher torque output, faster response time, and the ability to start and operate directly without additional excitation.
Front Axle Drive Unit (Compact Configuration)
- High-Performance PMSM Motor:
- 190 kW & 400 Nm @ Turbo S
- 175 kW & 300 Nm @ Turbo and 4S
- Max speed: 16,000 rpm
- Weight: 76 kg
- Single-Speed Gearbox:
- Coaxial layout
- Torque capacity: +450 Nm (traction), -300 Nm (regen braking)
- Two planetary gear sets
- Water-jacket cooling
- Weight: 16 kg
- Pulse-Controlled Inverter:
- 800V system
- 600A for Turbo S, 300A for Turbo and 4S
- Launch control output:
- Up to 440 Nm @ Turbo S
- 300 Nm @ Turbo
Rear Axle Drive Unit
- High-Performance PMSM Motor:
- 335 kW & 550 Nm @ Turbo S and Turbo
- 320 kW & 340 Nm @ 4S
- Max speed: 16,000 rpm
- Weight: 170 kg
- Two-Speed Transmission
- Pulse-Controlled Inverter with 800V High Voltage
Porsche Taycan Motor Hair-Pin Winding
Back in 2019, the Taycan’s adoption of hair-pin winding was considered cutting-edge. By 2025, it’s become a common feature in Chinese EVs.
The core of hair-pin winding lies in the shape of the copper wire used inside the stator. Unlike traditional windings that use round copper wire, Porsche uses rectangular-section copper bars tightly packed into the stator slots.
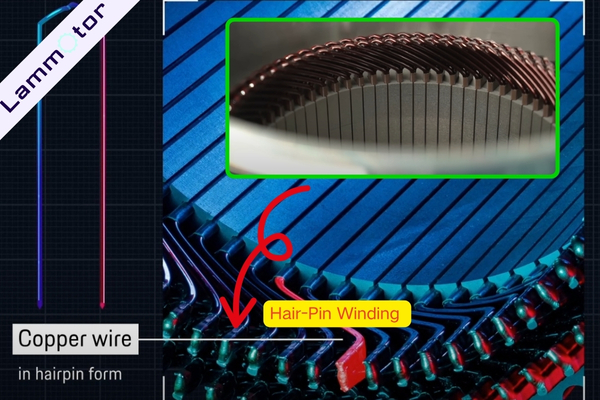
These copper bars are laser welded at the open ends to form complete coils.
This design makes the motor more compact, lighter, and more efficient, with higher torque and sustained power output.
Conventional round-wire windings typically achieve a copper fill factor of around 45%, while hair-pin windings reach up to 70%. A higher copper fill means lower resistance and less heat—resulting in greater power and torque in the same volume.
Moreover, the close contact between adjacent copper bars improves heat transfer, giving the stator excellent cooling performance. That’s why, back in 2019, the Taycan’s motor had one of the highest energy densities on the market.
Porsche Taycan Motor Cooling System
Both the front and rear motors are water-cooled PMSMs.
By 2025, most EVs have adopted oil-cooling for their flat-wire motors. Examples include Tesla’s Model Y and BorgWarner’s oil cooling systems.
Brief Comparison: Xiaomi SU7 Ultra V8s Motor
Before we wrap up, let’s briefly compare Porsche’s motor with the impressive Xiaomi SU7 Ultra. For more details, check out our full post on the Xiaomi SU7 motors.
The SU7 Ultra features a triple-motor setup: two in-house V8s motors (up to 27,200 rpm) and one jointly developed V6s motor with Inovance. Together, they produce a maximum output of 1548 PS.
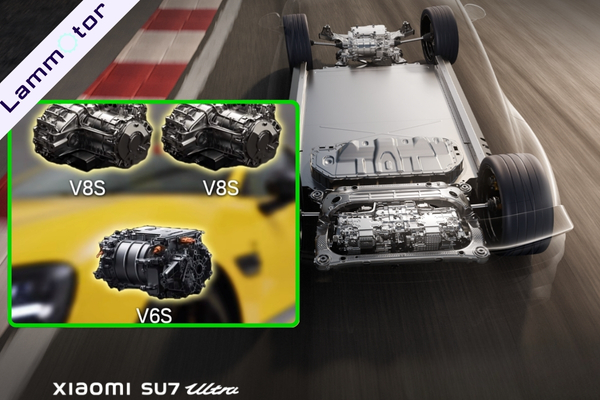

The result? 0–100 km/h in just 1.98 seconds and a top speed over 350 km/h—ranking it among the fastest four-door production cars in the world.
It also lapped the Nürburgring in 6 minutes 46.874 seconds (vs. Taycan’s 7 minutes 7.55 seconds). Even though the SU7 used a prototype body, the three-motor powertrain was made entirely from production-spec components—highlighting the car’s serious hardware and software capabilities.
In-House Motor Innovations from Xiaomi
The V8s motor features dual-direction full oil cooling and an S-shaped 3D oil circuit that directs coolant right to the stator windings and rotor shaft—boosting heat dissipation by 100%.
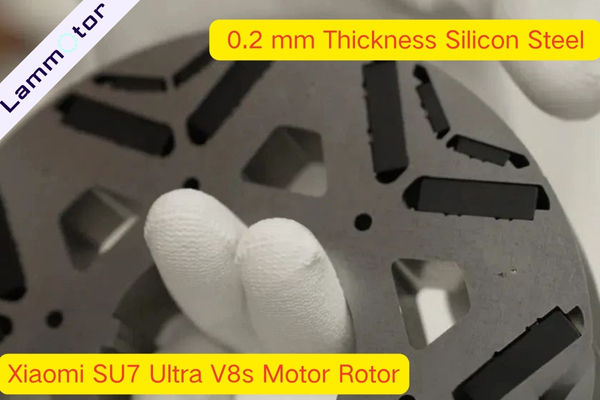
Xiaomi also uses ultra-thin laminated silicon steel (just 0.2 mm) and high-strength rotor materials to achieve ultra-high motor speeds. Their 27,200 rpm far exceeds typical industry standards—Tesla’s Plaid motor peaks around 20,000 rpm, and the Taycan maxes out at 16,000 rpm.
How Far Has EV Motor Tech Come?
From Porsche’s precise hair-pin winding to Xiaomi’s record-breaking motor speeds, electric vehicle motors have come a long way. Taycan’s motor was once a benchmark in 2019, but newer contenders are rapidly pushing the limits of performance, cooling, and packaging.
Which approach do you find more impressive—Porsche’s refined engineering or Xiaomi’s extreme output?
If you’re developing high-performance electric drive systems and need custom stator and rotor core manufacturing, we’d love to help.
We specialize in laminated stator and rotor cores for EV motors and offer prototyping, bonding, and laser welding services tailored to your needs.
Contact us today to explore how we can support your EV motor projects.