Have you ever thought all linear motors look the same? Think again! Choosing between Ironcore and Ironless Linear Motors is like choosing between a powerlifter and a ballet dancer—they both excel, but in completely different ways. Pick the right one and your production line runs smoothly. Pick the wrong one and you could face inefficiency or even downtime.
In this article, we’ll break down the key mechanical and electrical differences between Ironcore and Ironless Linear Motors, showing you how their structures, performance, and applications set them apart. By the end, you’ll know exactly which one fits your project best.
Ironcore Linear Motors
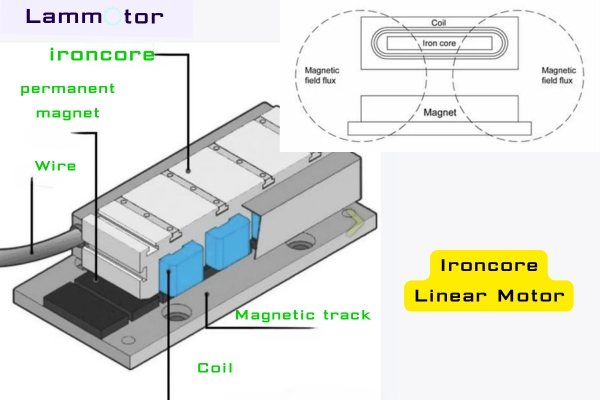
An Iron core Linear Motor uses laminated silicon steel (iron lamination) in its stator or mover. Coils are wound tightly around the laminations, and the magnetic circuit is reinforced by the iron core. This design provides strong thrust force, excellent rigidity, good thermal management, and lower production cost compared to its ironless counterpart.
Because of these characteristics, Iron core Linear Motors are widely used in heavy-duty applications such as CNC machine feed drives, elevator systems, and large industrial automation equipment where high thrust and load capacity are critical.
Ironless Linear Motors
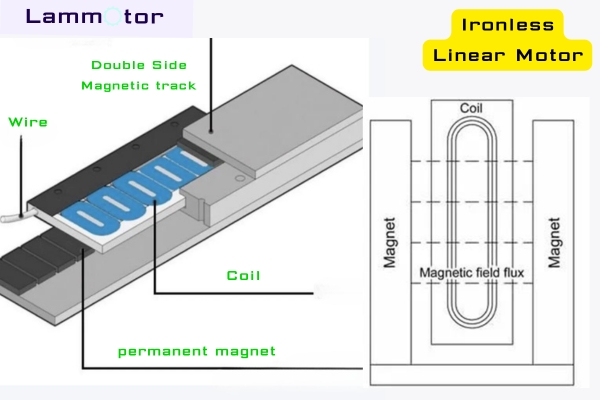
An Ironless Linear Motor eliminates the traditional laminated core. Its coils are encapsulated with epoxy resin into compact units, free from iron saturation or slotting effects. The result is a lightweight, modular design with smooth motion, no cogging, and very low noise.
This structure makes Ironless Linear Motors ideal for high-precision and high-speed applications such as semiconductor equipment, optical positioning systems, and advanced medical devices like CT scanners. Their low moving mass ensures rapid acceleration, ultra-fast dynamic response, and pinpoint accuracy.
Iron core Linear Motor Features
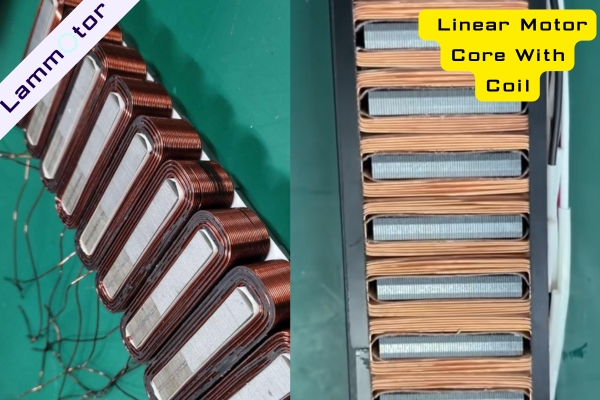

- High Thrust: Thanks to the iron core, an Ironcore Linear Motor can generate greater thrust, making it an ideal choice for moving heavy loads.
- High Rigidity: During machining and processing, its rigid structure ensures excellent accuracy and stability.
- Good Heat Dissipation: The iron core design helps dissipate heat, reducing operating temperature and improving reliability and service life.
- Lower Cost: Compared with Ironless Linear Motors, production costs are relatively lower since they do not require a large number of permanent magnets.
Ironless Linear Motor Features
- No Cogging Effect: With no iron core or slots, Ironless Linear Motors deliver smoother motion without the vibration and noise caused by cogging.
- High Acceleration: Their lightweight design allows higher acceleration and deceleration, perfect for applications that demand quick response.
- Easy Installation: The absence of strong attraction forces makes installation simpler and less labor-intensive.
- Modular Design: The magnetic circuit, formed by two rows of magnets, supports modular configurations, making expansion and customization easier.
Key Performance Comparisons
1. Thrust Characteristics
- Iron core Linear Motor: Strong thrust output due to reinforced magnetic coupling and reduced reluctance. Perfect for heavy loads, high acceleration, and demanding applications like machine tools and heavy automation.
- Ironless Linear Motor: Each coil unit generates smaller thrust, but multiple coils can be connected in series or parallel to scale performance. Best for light-load, high-precision needs such as wafer handling or optical alignment.
2. Speed Characteristics
- Ironcore Linear Motor: At high speeds, eddy current and hysteresis losses increase, causing heating and efficiency drops. More suited for medium-to-low speed with high force requirements.
- Ironless Linear Motor: No iron means no core losses. High efficiency even at high speeds, making them perfect for fast-moving automation lines and high-speed sorting systems.
3. Dynamic Response
- Ironcore Linear Motor: The iron core adds weight and inertia to the moving parts, slowing down start/stop response. Performance can be improved with design optimization and control algorithms.
- Ironless Linear Motor: Lightweight and low inertia allow for rapid acceleration, quick stops, and precise control. A strong choice for robotics joints and ultra-precise positioning platforms.
4. Application Scenarios
- Ironcore Linear Motor: Best for high thrust, medium-to-low speed uses—CNC feed systems, elevators, heavy automation.
- Ironless Linear Motor: Best for high precision, high speed, low noise uses—semiconductor tools, optical instruments, medical motion systems.
Conclusion
When comparing Ironcore and Ironless Linear Motors, the choice comes down to your application. If you need massive thrust and heavy load capacity, Ironcore is your solution. If you demand speed, precision, and smooth motion, Ironless is the way to go.
So, which linear motor core suits your project? Whether you are designing automation equipment, CNC machinery, semiconductor tools, or medical devices, making the right decision is key to success.
If you are looking for a trusted partner to manufacture linear motor cores tailored to your needs, contact us today. Our team specializes in producing high-quality Ironcore and Ironless Linear Motor cores to help you achieve the performance your application demands.