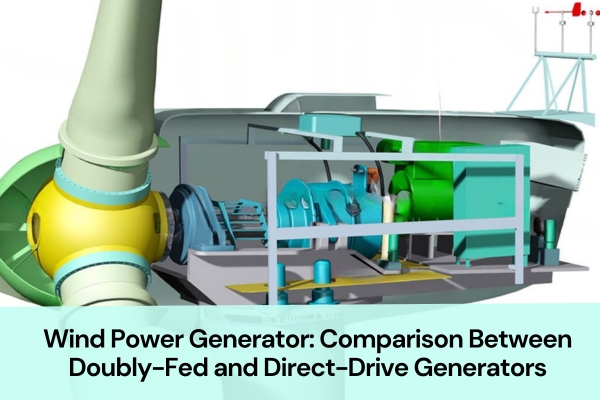
Why are there different types of wind power generator, and which one is more suitable for large-scale wind farms?
When people talk about renewable energy, wind turbines play an important role. Among the many types of wind power generators, the most common ones are the doubly-fed generator and the direct-drive permanent magnet generator.
As a manufacturer of generator stator and rotor cores, we have many years of experience and today I will explain these two types of generators and their main differences.
What is a Wind Power Generator?
A wind power generator converts wind energy into mechanical power. The rotor turns under wind force and finally generates alternating current electricity.
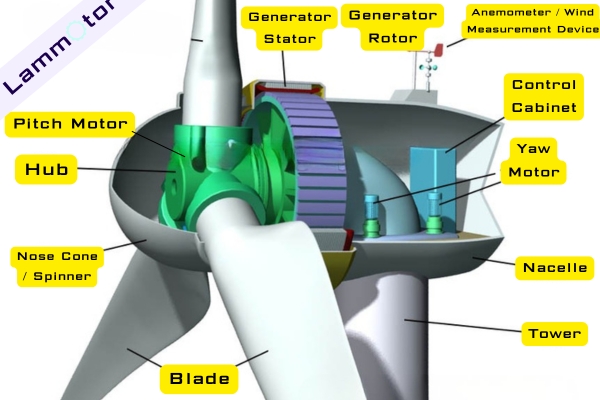
A typical wind turbine generator includes the wind rotor, generator (with its devices), yaw system (or tail vane), tower, safety system, and energy storage unit.
Wind power generators can be divided into doubly-fed generators, direct-drive permanent magnet generators, and semi-direct drive permanent magnet generators. Today, the two most widely used types are the doubly-fed wind power generator and the direct-drive permanent magnet wind power generator.
Doubly-Fed Wind Power Generator
A doubly-fed generator is an AC excitation generator. Its stator and rotor can both deliver energy to the grid. Both parts participate in excitation, and both can exchange energy with the grid.
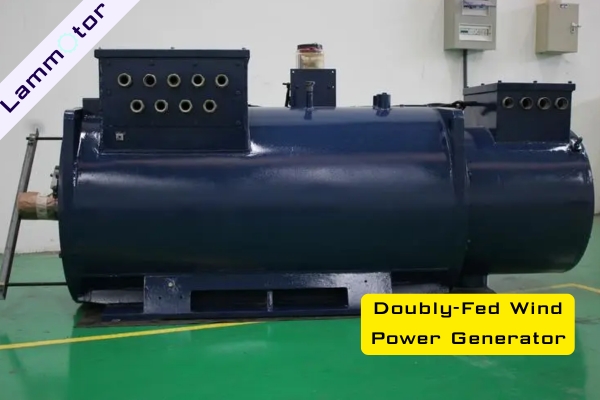
The doubly-fed wind turbine generator adopts a wound rotor induction generator, which is the core component of variable speed constant frequency systems.
Compared with traditional fixed-speed generators, this design achieves higher efficiency and adapts better to wind speed changes.
- It has higher starting torque, which ensures more stable operation during start-up.
- It covers a wider speed range, making it suitable for various wind conditions.
- It is cost-effective, reliable, and has become the mainstream choice in the wind turbine industry.
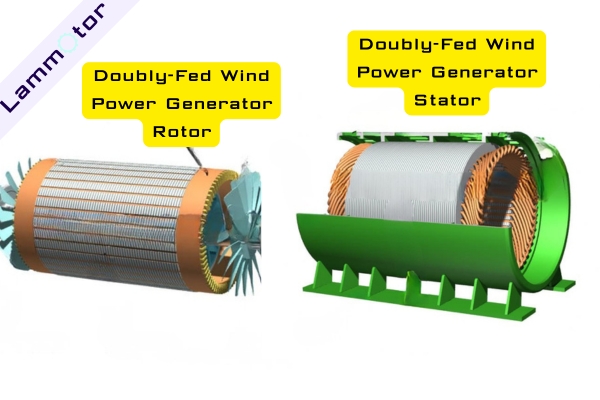
The stator winding connects directly to the grid, while the rotor winding connects to the grid through a converter. The converter regulates frequency, voltage, amplitude, and phase, allowing constant frequency generation at different speeds.
Main advantages of doubly-fed wind power generators include:
- Ability to control reactive power and decouple active and reactive power.
- Excitation comes from the rotor circuit, not from the grid.
- Capability to generate reactive power and deliver it to the stator through the grid-side converter.
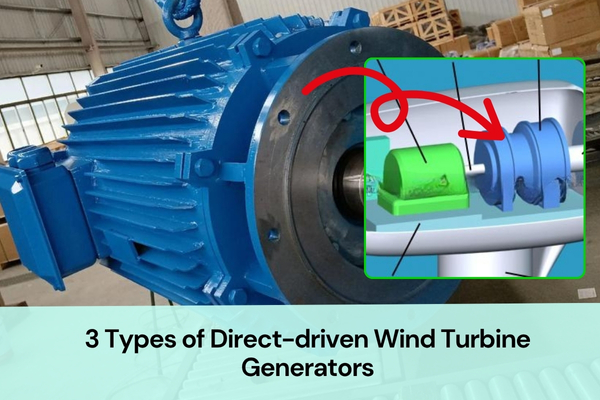
Direct-Drive Wind Power Generator
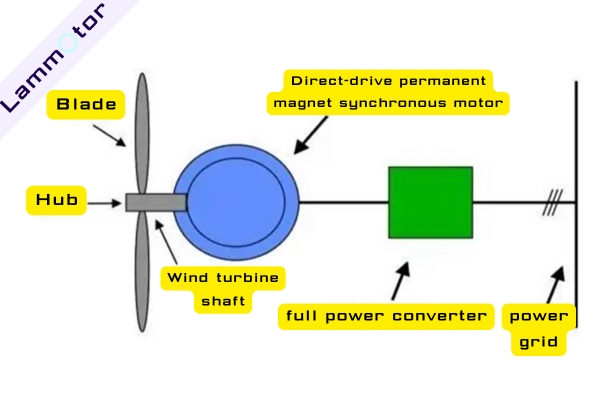
A direct-drive wind power generator connects the wind rotor directly to the generator, without a gearbox.
To improve efficiency, the number of poles is increased (often up to 100 poles) and a full-power converter is used for speed control.
Direct-drive generators can be electrically excited or permanent magnet types:
- Electrically excited direct-drive generators use the same working principle as hydro-generators. The technology is mature, and ENERCON (Germany) has achieved strong market results with it.
- Permanent magnet direct-drive generators replace the complex excitation system with permanent magnets. The structure is simple and the weight is lighter than electrically excited units.
A direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous wind power generator converts wind energy into electric energy with a simple, direct structure.
It consists of the generator, the wind rotor, and the support structure. It does not use a gearbox. The wind rotor connects directly to the generator rotor.
Wind turns the rotor and the generator produces power. This design cuts mechanical transmission loss and improves efficiency.
The direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous wind turbine generator has no gearbox, which reduces energy loss. The rotor connects directly to the generator, making the design simpler and more efficient.
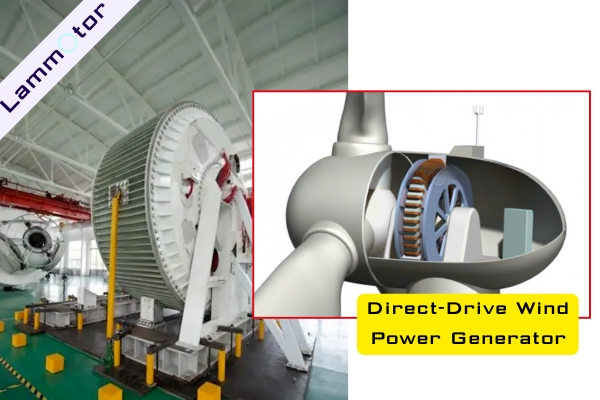
Advantages of direct-drive permanent magnet wind power generators:
- High efficiency – no gearbox reduces losses, especially at low wind speeds.
- High reliability – fewer rotating parts and no gearbox reduce failures.
- Low maintenance cost – no need for gearbox oil changes and fewer parts.
- Excellent grid performance – with low voltage ride-through ability, they can stay connected even during voltage drops.
Comparison Between Doubly-Fed and Direct-Drive Generators
- Doubly-fed generators need a gearbox; direct-drive generators do not.
- Converter size: doubly-fed uses ~1/3 rated capacity; direct-drive requires full rated capacity.
- Power flow: doubly-fed stator and rotor work differently below and above synchronous speed; direct-drive uses the stator across all speeds.
- Slip rings: required in doubly-fed (maintenance every 5–6 years); not needed in direct-drive.
- Maintenance: doubly-fed gearboxes require more service; direct-drive has simpler maintenance.
- Size: above 3 MW, doubly-fed gearboxes become large; direct-drive generators become very large and need split transport.
- Efficiency: direct-drive theoretically has higher efficiency, but actual performance depends on magnet material and air gap design.
- Cost: doubly-fed is cheaper due to high price of permanent magnet materials.
- Design challenges: direct-drive faces blade and tower clearance issues at larger scales.
Why is the Doubly-Fed Generator Still the Mainstream Model?
- Direct-drive generators are very large, making installation and transport difficult.
- They require extremely high standards for bearings and rotating parts.
- Permanent magnets risk demagnetization under vibration, shock, or high temperatures.
- Corrosion protection in offshore environments is still a challenge.
- On-site maintenance is not possible; generators must be returned to the factory.
- Direct connection between rotor and blades increases mechanical load and potential failures.
For these reasons, the doubly-fed wind power generator has become the mainstream solution in the wind energy industry today.
Wind Power Generator Stator And Rotor Lamination Manufacturer—Lammotor
Both doubly-fed and direct-drive wind power generators have unique advantages. Doubly-fed types dominate the market for their cost-effectiveness and easier maintenance, while direct-drive types offer higher efficiency and reliability, especially at low wind speeds.
Which type do you think is better for the future of wind energy—stability and cost, or efficiency and simplicity? Feel free to share your opinion with us.
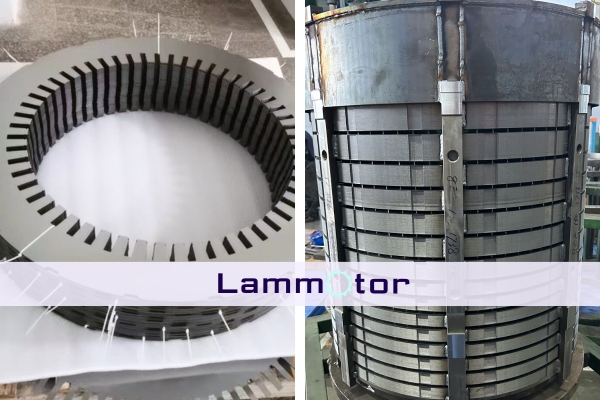

As a professional wind power generator stator and rotor core China manufacturer, Lammotor has extensive experience in producing high-quality lamination stacks for large wind turbines.
If you need custom-made stator or rotor cores for wind power generators, please contact us today.